How Air Starting System Works
- Assume Engine stops and air from receiver opens.
- Air passes to an automatic valve which remains closed as the air pressure acts on top of the piston.
- All cylinder valves and distributor valves are vented.
- When starting lever is moved to the position shown, then air from the top of the automatic valve is vented to the pilot starting valve.
- The automatic valve opens, the lower vent connection is closed and air flows to all cylinder and distributor valves.
- Air pressure (30 bar) at cylinder valve remains on standby till signal from respective pilot valve from the distributor.
- Number 6 unit pilot valve of the distributor is on the negative part of the CAM. This allows air to proceed to the number 6 cylinder unit and start the engine in the ahead direction.
- When the lever is moved to fuel position, the whole system is again vented to the atmosphere through The Automatic valve (by means of the lever )
- For astern running, reversing lever is moved over to allow switch cock to activate air piston to shift CAMSHAFT and to align with camshaft with negative cam to distributor pilot valve.
- The Pilot valve kept off the camp during reversing.
- Astern running follows with the movement of starting lever again.
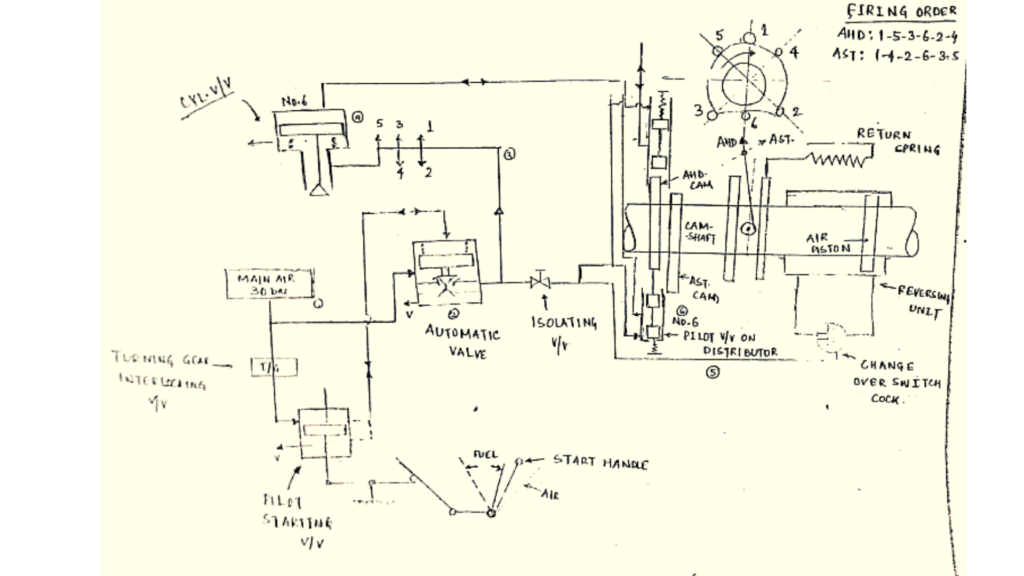
Table of Contents
ToggleSafeties incorporated in Air Starting System
- Running direction interlock– Here the Telegraph movement ensures the direction of rotation is in keeping with the bridge order.
- The turning gear interlock– Starting air to the engine is blocked by the valve when turning gear is engaged. This is a mechanical arrangement with limit switches to indicate position on the panel on the control room
- Assorted pressure switches for Lube oil, jacket cooling water, piston cooling water, turbocharger lubrication are also sometimes incorporated to block the starting
- Bursting disc
Methods of Starting
- Manual starting
- Rope and Pulley system (small diesel engine)
- Hand cranking (requires between 2 and 7 revolutions of the engine) lifeboat engines
2. Electric starting
- Battery operated
- Emergency generator
3. Pneumatic air motor starting
4. Direct air starting (common engines)
5. Hydraulic starting