Turbocharging is a concept in which the engine uses its own exhaust gas to generate compressed scavenge air for the main engine through the turbocharger (comprised of compressor and turbine ) thus increasing the overall efficiency of the engine. The reciprocating internal combustion engine is internally a pulsating device. Turbines can be designed to accept such unsteady flow but they operate more efficient under steady flow conditions. In practice, two approaches for recovering a fraction of the available exhaust gas energy are commonly used .
Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of Turbocharging in Engines
- Constant pressure turbocharger
- Pulse-type turbocharger
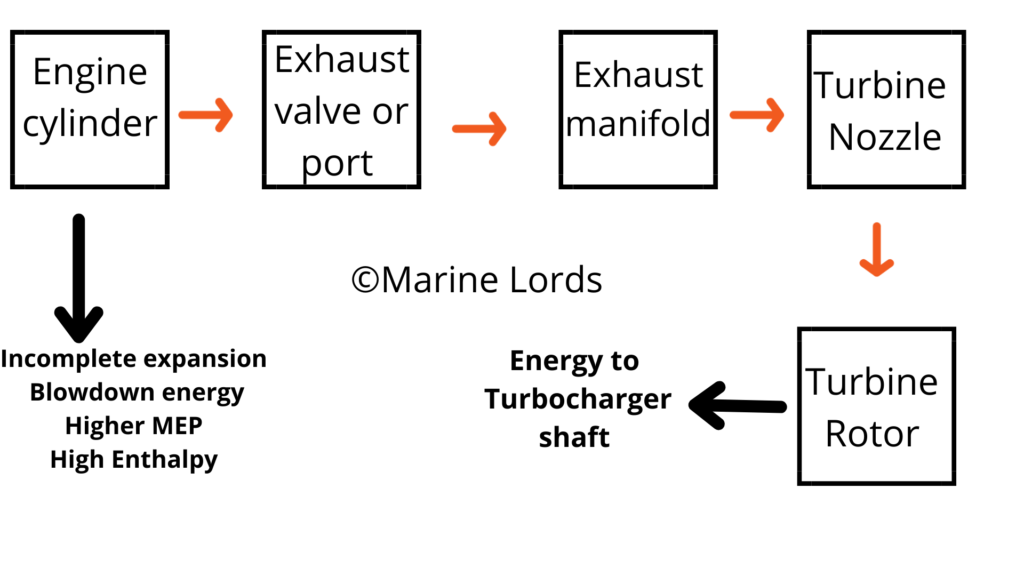
In constant pressure, an exhaust manifold of sufficiently large volume is used to damp out the mass flow and pressure pulses, so that the flow to the turbine is essential steady.
With Pulse Turbocharging system short, small cross-sectional pipes are used which are connected from each exhaust port through the turbine so that much of the internal combustion associated with the exhaust blowdown can be utilized.
Constant Pressure Turbocharger
- Exhaust gas from all cylinders passes into a common large manifold where pulse energy is converted into pressure energy in reserve.
- Through the Exhaust valve or port exhaust gas is throttled from cylinder to large diameter exhaust manifold where gas expand.
- As the mean effective pressure is increasing with the diesel engine development, the enthalpy constant is considerably more in the exhaust gas.
H=U+PV
* where H= Enthalpy, U= Internal energy, P & V are pressure and volume.
4. High turbine efficiency is due to the study flow of mass.
5. Exhaust gas expands through a nozzle (from constant pressure) and enthalpy drop ( over turbine blade area ) finally energy transfer to turbocharger shaft.
Advantages of constant pressure turbocharging
- Better or more rational utilization of exhaust heat
- Good performance for high load operation
- It is more suitable for high rating engine
- No exhaust pressure Pulse are required
- Grouping of exhaust outlet or exhaust turning is not required
- The piping system is simple.
- High turbine efficiency due to study flow of mass
- Reduction in specific fuel oil consumption.
Disadvantages of constant pressure turbocharging
- During load change poor turbocharger acceleration
- During part load ( no load operation) when energy is low as exhaust temperature and quantity are less , system requires additional arrangement for charged air ( Auxiliary blower )
- The system requires an auxiliary blower cut off arrangement at high load
- As exhaust manifold is of large diameter , engine requires more space to install
