- In Pulse-type Turbocharging system, it makes full use of the high pressure and temperature of the exhaust gas during the blowdown period and rapidly opening of the exhaust valve.
- The Exhaust gas reaches the cylinder at extreme velocity as pressure energy is transformed into kinetic energy to form a pressure wave or pulse in the exhaust Pipe and it eventually lead to the turbocharger turbine.
- The exhaust pipe so constructed in small diameter is quickly pressurized and boosted up to form pressure pulses or waves.
- The Pressure wave reached to turbine nozzle and further expansion takes place.
- Some interference may exist between exhausting and scavenging among cylinders.
- The exhaust pipes are grouped or tuned such as to prevent any possibility of exhaust going into another cylinder during the scavenging period.
- The pipes are organised in lesser diameter to increase up pressure pulses and used in little lengths that are straight to prevent energy losses.
- No sharp bends in the pipe are provided, and neither is any obstruction on the exhaust pulse flow.
- The number of exhaust branches depends on a firing order, number of cylinders and turbocharger design.
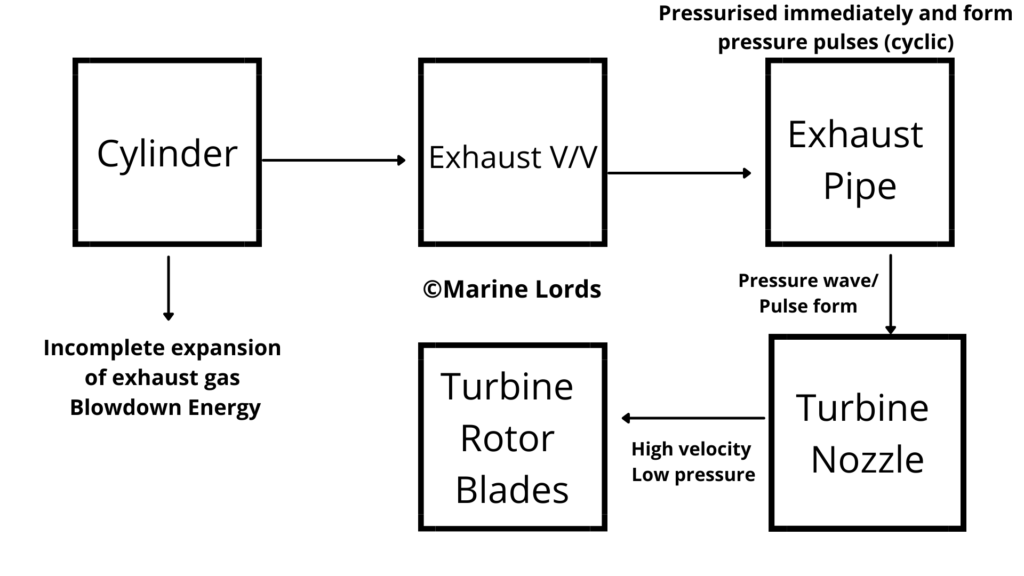
Table of Contents
ToggleAdvantages of Pulse-type Turbocharging system
- At reduced load and reduced speed, more efficiency can be seen.
- At a low load, it does not require any form of scavenging assistance.
- During load change, good turbocharger acceleration and response is there.
- High energy is available at the turbine inlet.
- The system does not require a larger volume to accommodate the exhaust pipe inside as it does not require a large diameter manifold.
Disadvantages of Pulse-Type Turbocharging system
- The exhaust grouping is complicated and quite complex in design.
- Very unique sizes of exhaust pipes are required for spare.
- Pressure wave reflection problems may be caused in some engines.
- Poor Turbine efficiency at a very high rating
- Firing order, number of cylinders, number of turbochargers must be considered during exhaust grouping.