Leading maritime community ! [email protected]

Uptakes are passages through the engine room funnel which allows exhaust gases from –
The exhaust gas boiler consists of tube stacks with fins for maximum heat transfer and efficiency. The exhaust gas from the main engine and auxiliary boiler flows through the tube stacks. Poor combustion of fuel leads to carbon formation in the soot form.
Soots are carbon particles and are polar in nature (i.e each particle have south and north pole) and forms cluster through agglomeration.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe uptake fire is distinguished in stages rather than type. these are three stages and depending on the intensity of Fire, they are classified as
The potential ignition temperature of soot fire is in the region of 300 degrees Celsius to 400 degrees Celsius. But the presence of oil may lower it to 150 degrees Celsius and extreme cases to 220 degrees Celsius .this means soot fire may take place even after the shutdown of the main engine. As a result of glowing particles remaining on the fins of the boiler tube.
This soot fire is called small and normal soot fire because that heat energy is conducted away by circulating boiler water and steam in the pipes.
The spark remain inside the funnel and diminished oil particles passing through the flame arrestor.
This occurs when the dissociation of water takes at a temperature of 1000 degrees Celsius.
If a large quantity of soot settles as heavy carbon deposit and these smouldering carbon burns are passed over with exhaust gases with oxygen, will cause temperature rise to 900 degree Celsius. This may cause tube failure and water leakage. Water in such places dissociates to give hydrogen and carbon monoxide both of which are combustible. Alternatively, soot blowing with steam at this stage will result in similar consequences.
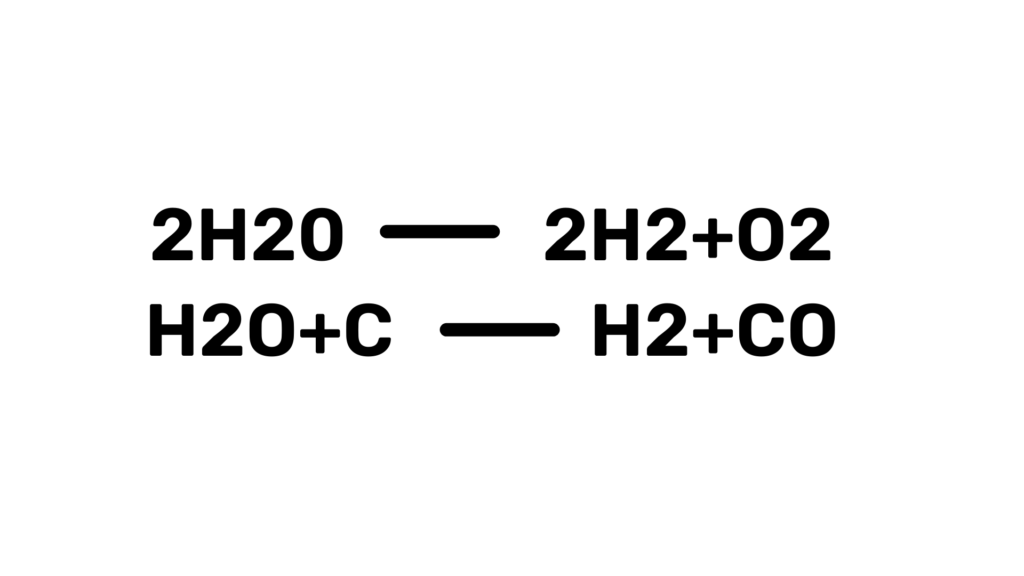
At this stage, a chain reaction of oxidation of iron metal starts at a high temperature of 1100 degrees Celsius, which means at such a high temperature the iron tube will start burning itself at a rate high enough to make the amount of heat release from the reaction sustain the process. This reaction may take place in excess of 1100 degrees Celsius.
Note:- Do read our article on Engine Scavenge Box Fire