The weldability is the capacity of being welded into indivisible joints having certain characteristics such as weld strength, correct structure etc. that relies upon –
- Melting point
- Thermal conductivity
- Thermal expansion
- Surface condition
- Change in microstructure
Table of Contents
ToggleDifferent types of welding ?
There are basically two types of welding –
- Pressure welding
- Non-pressure welding
- Pressure welding or Forge welding– Any welding process which requires pressure is generally referred to as a forge welding process and these processes does not usually require a filler metal or flux.
The process comprises of heating the metallic components to be welded in a fire until the parts to be united are plastic, then the parts of the components are removed from the temperature source and beaten together to form a combination.
Resistance welding is a forge welding process, current and pressure are applied to the parts being welded but filler metal or flux is not required. The heat generated in order to form the weld depends upon-
- Square of the current applied.
- Metal to be welded and contact resistance.
- Time of application of current.
- Fusion welding – Welding process which does not require any pressure and the process requires a filler metal and often a flux is used.
Most popular is an electric arc welding –
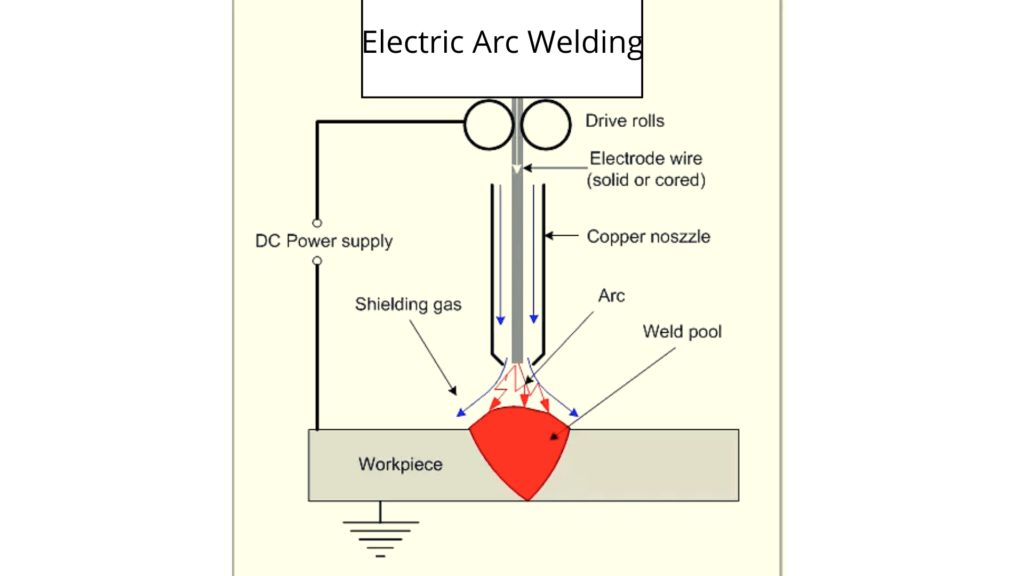
Electric Arc Welding
In this process, an electric arc is struck between the electrode, which may serve as the filler material and the metal to be welded. The heat generated causes the electrode to melt and the molten metal is then moved from that electrode to the plate.
The arc stream is open to contamination from the atmosphere and this result in a porous brittle weld. To avoid these non-uniformities, flux coated electrodes are mostly used.
The flux coating protrudes beyond the cone since it melts at a higher temperature than the electrode metalcore. It gives good stability, control and intensity of the arc. The coating also shields the arc and the molten metal pool from the atmosphere by means of the inert gas shield given off as it vapourises.
The silicates that are shaped from the coating, shape a slag upon the surface of the hot metal and this protects the hot metal from the ambience as it cools down.